The Dutch Defense is a flank opening that Black employs to gain control of the e4 square right from move 1. It is an uncommon way to reply to the queen’s pawn opening.
The Dutch Defense starts with 1. d4 f5.

After White develops their queen pawn, they gain control of the central e5 square.
Black, in the Dutch, does not fancy playing popular continuations like …d5 or ….Nf3. Rather they go for the Dutch defense with f5 and stake their claim to the e4 square.
The Dutch is an exciting opening as it creates an imbalance in the position while maintaining flexibility for Black. It is also not a very popular opening, as very few players play it.
There are three major variations of the Dutch, they include:
- Classical Dutch
- Leningrad Dutch
- Stonewall Dutch
Classical Dutch
1. d4 f5 2. Nf3 Nf6 3. g3 e6 4. Bg2 Be7 5. 0-0 0-0 6. c4 d6
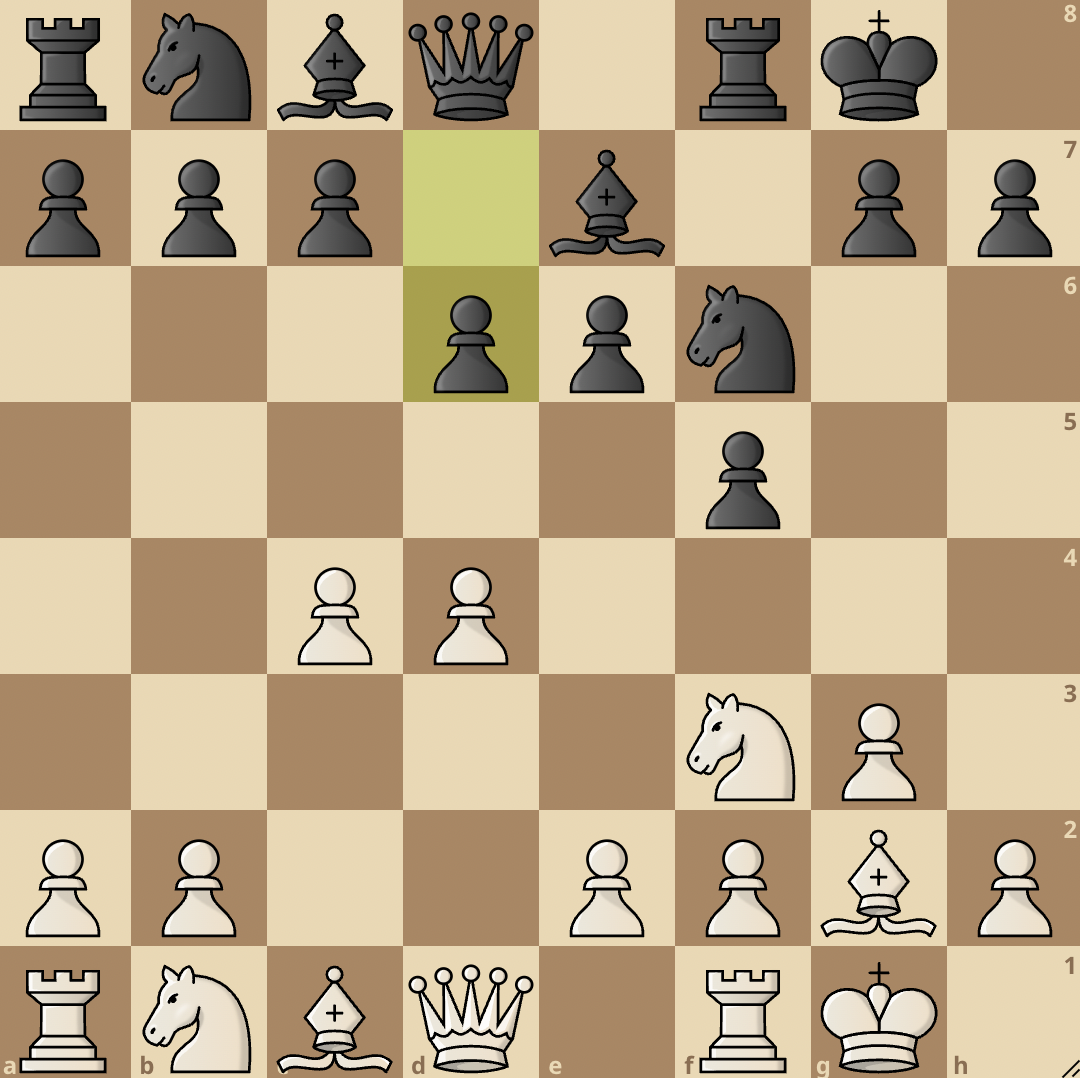

The Classical variation is a popular variation of the Dutch. Here, Black constructs a solid setup with a castled king and a good grip on the e4 square.
To arrive at the classical Dutch, Black starts by playing …f5 as a response to White’s d4. White then develops their knight to f3 to help strengthen their hold on the e5 square.
Black also plays 2. Nf6, with a similar idea of controlling the e4 square. White needs to develop their light-squared bishop, however, they can’t play e4 as the e4 square is under Black’s control…playing e3 also locks in the dark-squared bishop, so the best continuation for White here is to play 3. g3 and fianchetto their bishop.
Black will continue with 3…e6, adding support to their f5 pawn and opening lines for their dark-squared bishop.
White then fianchettoes their bishop with 4. Bg2 and Black develops their dark-squared bishop with 4…Be7.
Both sides castle with 5. 0-0 0-0 and White grabs more space in the center with 6. c4. Black now plays the move 6…d6 and this signifies the start of the classical Dutch.
In this position, we can see that Black has a firm grip on the e4 square, they also have a castled king and their knight can come into the game.
The light-squared bishop would be developed via the b7 square to contest against White’s bishop on g2.
Black will most likely go for a kingside attack and try to get through the White’s king defenses, while White will look to dominate on the queenside.
Leningrad Dutch
1. d4 f5 2. Nf3 Nf6 3. g3 g6 4. Bg2 Bg7 5. 0-0 0-0 6. c4 d6

The Leningrad Dutch is perhaps the most played variation of the Dutch Defense. It starts with the usual 1. d4 f5 2. Nf3 Nf6.
After 3. g3, Black does not play…e6 like in the classical variation, rather they decide to play 3…g6 and fianchetto their dark-squared bishop.
This results in some sort of symmetry on the kingside since both kingside bishops are fianchettoed.
Both sides then fianchetto their bishops with 4. Bg2 Bg7. Castling also follows for both White and Black with 5. 0-0 0-0.
White continues with 6. c4, looking to grab more space and Black plays 6…d6. White then develops their knight with 7. Nc3 and Black plays 7…Qe8.
By playing …Qe8, Black prepares to strike in the center with…e5 and create tension in the position.
White will usually play 8. d5 to stifle the advance of the e-pawn. If this happens, Black will shift play to the queenside and look for an advantage there.
Stonewall Dutch
1. d4 f5 2. g3 Nf6 3. Bg2 e6 4. c4 d5 5. Nf3 c6

The Stonewall Dutch is another variation of the Dutch that’s played by very strong players like the former world champion Magnus Carlsen.
It starts with 1. d4 f5. White then prepares to fianchetto their bishop and they play 2. g3, Black replies with 2…Nf6.
3. Bg2 follows and Black opens up lines for their dark-squared bishop with 3…e6. White now plays 4. c4 and Black plays 4…d5.
After 5. Nf3, Black plays 5…c6, starting the Stonewall Variation. White then castles and Black completes the Stonewall with 6…Bd6.
In the Stonewall, Black gets a solid pawn structure and after safely tucking their king beside their rook, they can begin formulating plans to launch a kingside attack.
However, the drawback of this variation is that Black will have a hard time developing their light-squared bishop. One way they can go about it is by playing …b6 and then …Ba6.
If the opportunity for a trade comes, Black will be more than happy to trade off their bishop for another piece.
Black’s best piece at the start of the Stonewall is their dark-squared bishop and White will look to trade it off and dull Black’s attacking chances.
Hopton Attack
1. d4 f5 2. Bg5

The Hopton is a rare variation of the Dutch that starts with 2. Bg5.
White’s idea here is to stifle Black’s normal development in the Dutch by pinning down the e-pawn. This move disrupts Black’s normal plans in the Dutch.
If Black decides to play 2…Nf6, White will capture the knight and ruin Black’s pawn structure. The best way to continue is for Black to play 2…g6, fianchetto their bishop and then play Nf6.
If Black tries to kick away the bishop with 2…h6, they will weaken their kingside. By playing…h6, Black might even fall into a trap that ends in checkmate if they are too persistent and try to get rid of the bishop by all means.
An example of how this can happen is 2…h6 3. Bh4 g5 4. Bg3 f4 5. e3 fxg3 6. Qh5#.
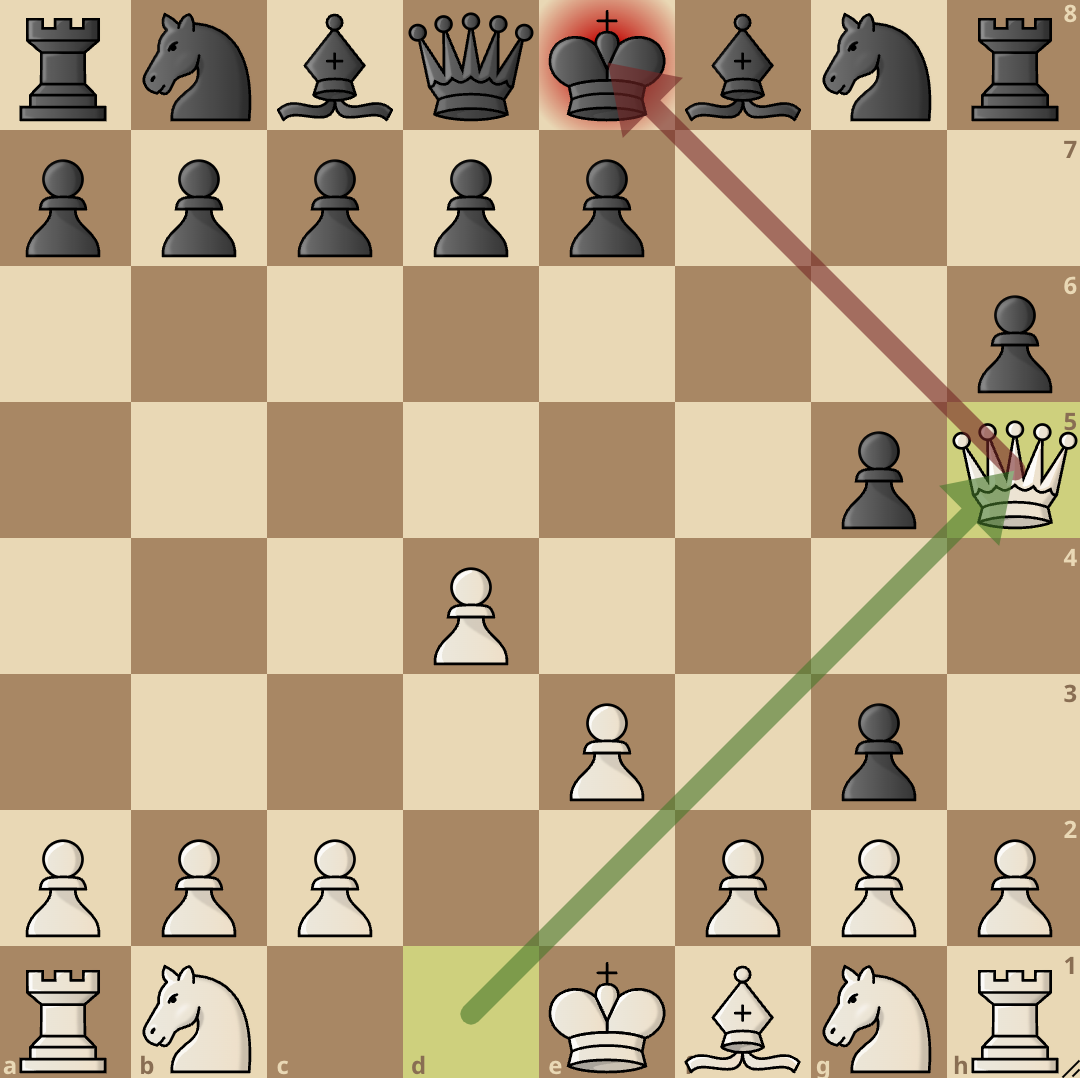
This just shows how risky it can be if Black tries to dislodge the bishop from g5 by force.
The Hopton Attack is a tricky variation Black can encounter and they need to be careful not to fall victim to its dangerous trap.
Successful Deployments
Touch the moves or move the board around for a better interactive experience.
Andrew Boekhoff v Hikaru Nakamura, North American Open (2006)
Hikaru Nakamura is an exciting player who loves to catch his opponents unawares and get the best of them. In the 2006 North American Open, he employed the Dutch Defense against Andrew Boekhoff and won a very nice game.
Alexander Alekhine v Savielly Tartakower, San Remo (1930)
While the Dutch is an opening that can be used to catch your opponents unawares, it wouldn’t faze a world champion and we saw a live demonstration of how a world champion beat the Dutch when Alexander Alekhine took down Savielly Tartakower in 1930.
Salvijus Bercys v Hikaru Nakamura, Foxwoods Open (2007)
Hikaru is an expert on many openings, and the Dutch is not an exception. Enjoy his 2007 win against Salvijus Bercys at the Foxwoods Open tournament.



join the conversation